[Linux Server] Monitoring and Logging User Commands in Bash with Telegram Bot
In this blog post, we’ll dive into a Bash script that enables you to monitor and log user commands executed in the terminal and send real-time notifications to a Telegram bot. This script proves invaluable for keeping track of important commands and receiving instant alerts when specific commands are executed, enhancing your system monitoring and security capabilities.
Prerequisites
Before we embark on this journey, ensure that you have the following prerequisites in place:
- A Unix-based operating system (e.g., Linux, macOS. Now I’m using in an environment of Ubuntu 22.04 LTS with GNU/Linux 5.15.0-102-generic x86_64)
- Bash shell
- Telegram bot token and chat ID
Creating a Telegram Bot and Obtaining Token and Chat ID
To create a Telegram bot and obtain the necessary token and chat ID, follow these steps:
- Open the Telegram app and search for the “BotFather” bot.
- Start a conversation with the BotFather by sending
/startand send the/newbotcommand to create a new bot. - Provide a name and username for your bot as prompted by the BotFather.
- Upon successful creation, you will receive an API token for your bot. Make sure to keep this token secure and confidential.
- To obtain the chat ID, follow these steps:
- Start a conversation with the “IDBot” bot.
- After sending
/start, send the/getidcommand to obtain the chat ID. - The chat ID will be displayed in the chat window. Make sure to keep this chat ID secure and confidential.
With the Telegram bot token and chat ID in hand, you’re ready to proceed with the script.
Script Breakdown
Let’s dive into the script and understand its core components:
ignore_commands="cd pwd ls htop top df du free uptime who w uname cat more less tail head grep find ping netstat ifconfig traceroute nano"
last_command=""
log_command() {
# current time
local current_time=$(date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
# user name, working directory, command history
local user_name=$(whoami)
local working_directory=$(pwd)
local command_history=$(history 1 | sed 's/^[ ]*[0-9]*[ ]*//;s/^[^]]*][ ]*//;s/^ *//')
local command=$(echo "$command_history" | awk '{print $1}')
# ignore empty command
if [[ -z "$command_history" || "$command_history" == "$last_command" ]]; then
return
fi
# last command update
last_command="$command_history"
# ignore commands in ignore_commands
for ignore_cmd in $ignore_commands; do
if [[ "$command" == "$ignore_cmd" ]]; then
return
fi
done
# message
local message="Time: $current_time"$'\n'"User: $user_name"$'\n'"Directory: $working_directory"$'\n'"Command: $command_history"
# Telegram Bot
curl -s -X POST "https://api.telegram.org/bot<API_TOKEN>/sendMessage" --data-urlencode "chat_id=<CHAT_ID>" --data-urlencode "text=$message" >/dev/null 2>&1
}
# PROMPT_COMMAND log_command
PROMPT_COMMAND="log_command; $PROMPT_COMMAND"
-
ignore_commands: This variable holds a list of commands that should be excluded from logging. These command lists are those which doesn’t modify files or the system. Modify this list based on your specific requirements, including commands that you don’t want to monitor or log. -
log_command(): This function serves as the heart of the script, responsible for logging user commands and sending notifications to the Telegram bot.- It captures the current time, user name, working directory, and the last executed command from the command history using various Bash commands and utilities.
- It extracts the command name from the command history using
awk, allowing for more fine-grained control over command matching. - It performs checks to ignore empty commands or commands that are identical to the previously logged command, preventing redundant logging.
- It updates the
last_commandvariable with the current command, ensuring accurate tracking of command history. - It iterates over the
ignore_commandslist and verifies if the current command matches any of the ignored commands. If a match is found, the function returns without logging the command. - It constructs a well-formatted message string containing the timestamp, user name, working directory, and the executed command, providing valuable context for each logged command.
- It sends the message to the specified Telegram bot using the
curlcommand, leveraging the Telegram Bot API to deliver real-time notifications.
-
PROMPT_COMMAND: This special Bash variable is set to execute thelog_commandfunction every time a command is executed in the terminal. By appendinglog_commandtoPROMPT_COMMAND, we ensure that the logging functionality is triggered seamlessly after each command execution.
Implementing the Script
To put this script into action, follow these steps:
-
Replace the placeholder Telegram bot token and chat ID in the script with your own values obtained from the BotFather and IDBot.
-
Save the script to a file with a descriptive name, such as
command_logger.sh. -
Open your Bash configuration file (e.g.,
.bashrcor.bash_profile) using a text editor:nano ~/.bashrc -
Add the following line at the end of the file to source the script:
source /path/to/command_logger.shReplace
/path/to/command_logger.shwith the actual path to the script file. -
Save the changes and exit the text editor.
-
Restart your terminal or run the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.bashrc
With these steps completed, the script will now log user commands and send notifications to your Telegram bot whenever a command is executed in the terminal, excluding the commands specified in the ignore_commands variable.
You know what? You can become a BIG BROTHER if your root. Just use /etc/bash.bashrc file instead of .bashrc or .bash_profile. It will allow you to monitor the bash terminal usage of all users!!
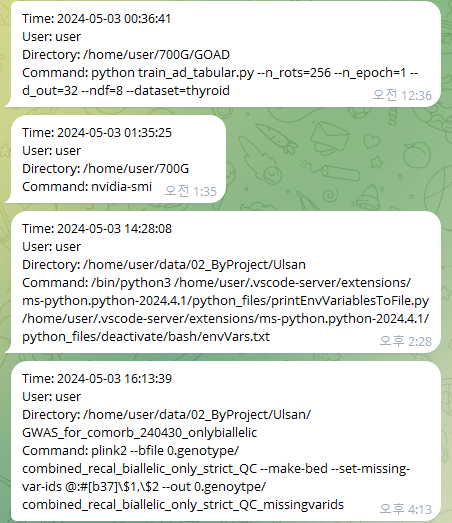
This is the example of the telegram bot monitoring:
Customization Possibilities
This script provides a solid foundation for monitoring and logging user commands, but it can be further customized to suit your specific needs:
- Modify the
ignore_commandsvariable to include or exclude commands based on your monitoring requirements. This allows you to focus on specific commands of interest while ignoring routine or less important commands. - Adjust the message format in the
log_command()function to incorporate additional information or modify the structure of the notification message. You can include system metrics, user-specific details, or any other relevant data to provide more comprehensive insights. - Extend the script to perform additional actions based on specific commands or patterns. For example, you can trigger alerts, execute automated tasks, or integrate with other monitoring or security tools when certain commands are detected.
- Implement additional security measures, such as encrypting sensitive information or using secure communication channels, to protect the integrity and confidentiality of the logged data and notifications.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored a powerful Bash script that enables monitoring and logging of user commands executed in the terminal, along with real-time notifications sent to a Telegram bot. By leveraging this script, you can gain valuable insights into command execution, enhance system monitoring, and improve security practices.
Remember to handle the logged data responsibly and ensure that it aligns with your organization’s security policies and privacy regulations. Regularly review and analyze the logged commands to identify potential security risks, unauthorized access attempts, or suspicious activities.
We encourage you to customize and extend the script based on your specific requirements, integrating it seamlessly into your existing monitoring and security infrastructure. By staying vigilant and proactive in monitoring user commands, you can strengthen your system’s security posture and maintain a robust and reliable environment.
Happy coding!

Leave a comment